Introduction
Moisture sensors are electronic devices designed to measure and monitor the moisture content of various substances or environments.
- Here we show the circuit diagram of the moisture sensor and how actual the sensor work we take an image from the datasheet.
- These sensors use agriculture, construction, food processing, and environmental monitoring. In this article, we will explain the workings of moisture sensors, types, applications, and how you interface with any microcontroller.
Working Principle of Moisture Sensors
Moisture sensors operate on the principle of measuring the electrical is find out the moisture level present in the moisture content. The moisture sensor methods used are resistive and capacitive sensing.
- Resistive Moisture Sensors: Resistive moisture sensors measure the electrical resistance of a material, which changes with variations in moisture levels. These sensors typically consist of two electrodes embedded in or attached to a moisture-sensitive material.
- Capacitive Moisture Sensors: Capacitive moisture sensors utilize the property of capacitance to measure moisture levels. These sensors comprise two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material, which can be a substance that absorbs or repels moisture.
Specifications of the Soil Moisture Sensor
- Measurement Range: That indicates the minimum and maximum moisture levels they can accurately detect. The range is usually expressed as a percentage water content value.
- Accuracy: it is expressed as a percentage or a VWC value and indicates the sensor’s deviation from the true moisture content.
- Sensor Type: There are various types of soil moisture sensors available, including resistive, capacitive, and frequency domain sensors.
- Installation Depth: Soil moisture sensors are often designed to be inserted into the soil at a specific depth.
- Response Time: Faster response times are generally preferred for real-time monitoring and control applications.
- Output Interface: Such as analog form and digital form.
Advantages of the Soil Moisture Sensor
- Water Conservation
- Improved Plant Health and Yield
- Cost Savings
- Environmental Impact
Disadvantage of the Soil Moisture Sensor
- Cost
- Calibration and Maintenance
- Sensor Variability
- Installation and Placement
Application of the Soil Moisture Sensor
- Soil moisture sensors are extensively used in agriculture for irrigation management.
- Soil moisture sensors are valuable in horticulture and landscaping applications, such as gardens, nurseries, and turf management.
- Soil moisture sensors are used in environmental research and monitoring programs to study the water content of soil in ecosystems.
- Soil moisture sensors play a role in construction and civil engineering projects.
Example with Arduino
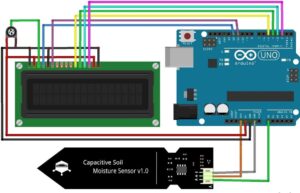
Now we interface the Capacitive moisture sensors and Resistive moisture sensor with Arduino and display the reading in the serial monitor and 16×2 LCD display.
Circuit Diagram with capacitive moisture sensors
Code with 16×2 LCD Display
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2); const int AirValue = 600; const int WaterValue = 350; int soilMoistureValue = 0; int soilmoisturepercent = 0; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); lcd.begin(16, 2); } void loop() { soilMoistureValue = analogRead(A0); Serial.println(soilMoistureValue); soilmoisturepercent = map(soilMoistureValue, AirValue, WaterValue, 0, 100); if (soilmoisturepercent >= 100) { Serial.println("100 %"); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Soil Moisture"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("100 %"); delay(250); lcd.clear(); } else if (soilmoisturepercent <= 0) { Serial.println("0 %"); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Soil Moisture"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("0 %"); delay(250); lcd.clear(); } else if (soilmoisturepercent > 0 && soilmoisturepercent < 100) { Serial.print(soilmoisturepercent); Serial.println("%"); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Soil Moisture"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print(soilmoisturepercent); lcd.print(" %"); delay(250); lcd.clear(); } } |
Circuit Diagram with Resistive moisture sensors
Code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
//Prateek #include <Wire.h> #include <LiquidCrystal.h> LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7); int m; int percentage; int led = 13; int map_low = 1023; int map_high = 280; void setup() { pinMode(A5, INPUT_PULLUP); pinMode(4, OUTPUT); pinMode(5, OUTPUT); Serial.begin(9600); lcd.begin(16, 2); lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Irrigation Systm"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("Pump="); lcd.setCursor(10, 1); lcd.print("M= "); } void loop() { int m = analogRead(A5); Serial.println(m); percentage = map(m, map_low, map_high, 0, 100); lcd.setCursor(10, 1); lcd.print("M= "); if (percentage > 100) { percentage = 100; } lcd.setCursor(12, 1); lcd.print(percentage); lcd.print("%"); lcd.print(" "); delay(200); if (m >= 780) { digitalWrite(4, HIGH); lcd.setCursor(6, 1); lcd.print("ON "); digitalWrite(led, LOW); } else if (m <= 770) { digitalWrite(4, LOW); lcd.setCursor(6, 1); lcd.print("OFF"); digitalWrite(led, HIGH); } } |
Video
Conclusion
Moisture sensors play a vital role in measuring and monitoring moisture content in various substances and environments. They provide valuable data for optimizing irrigation practices, preventing water wastage, and promoting healthy plant growth.
Sensor