Introduction
Hi Everyone, In this Tutorial, we will make a wifi-based control car Based on the New Blynk2.0 App. Nowadays day Robotics technology is used in various fields new designed Come to day by day.
Mostly wi-fi networks were using various applications. The various applications are done by robot cars like IOT IOT-based grass Cutters, IOT-based firefighters, IOT-based wheelchairs, and IOT-based agricultural robot cars.
in this Article, we will discuss how you set up the Blynk app and interface the l298n motor driver to ESP8266. With the help of this article, you make many Robot Car Projects.
If You are interested in More Projects Plz Check them out Here
Bill Of Materials
These are All Components Required to make this project and also we will give all short component Details.
S.N | Component's | Quantity | Link To Buy |
1 | ESP8266 | 1 | |
2 | L298N Motor Driver | 1 | |
3 | BO Motor | 2 | |
4 | BO Motor Wheels | 2 | |
5 | DC Female Jack | 1 |
ESP8266
ESP8266 is an IoT module-based WiFi Module Microcontroller. ESP8266 uses Lua Scripting language and is an open-source Internet of Things (IoT) platform.
Specification:-
- Integrated GPIO, PWM, IIC, 1-Wire, and ADC all in one board.
- USB-TTL included plug&play
- 10 GPIO, every GPIO can be PWM, I2C, 1-wire
L298N Motor Driver
The L298N Dual H-Bridge motor driver is a low-cost motor driver board in the market that can drive 4 motors it uses the popular L298N dual H-Bridge Motor Driver chip & is also powerful enough to drive motors from 5-35 volts at 2 amps per channel.
Features –
- Dual H-Bridge Motor driver Chip L298N
- 5V Regulator Poer Source
- Easy to interface with the most robot controller
- Drives motor from 5-35 at up to 2A Per circuit.
BO Motor
- This Bo motor Operates from 3-12V And Provides an impressive torque of 49 oz- in at just 5V.
- The Current consumes 40mA at 5V When free running at 24 rounds per minute.
- The shaft on the Motor Is 7mm.
- The Gear motor Has a 224:1 Gear ratio with a 90-degree output Shaft.
BO Motor Wheels
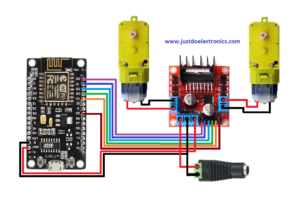
Circuit Diagram
A Circuit Diagram of a Grass Cutting Robot using ESP8266 Board. would Show the connections Between the different components of the robot.
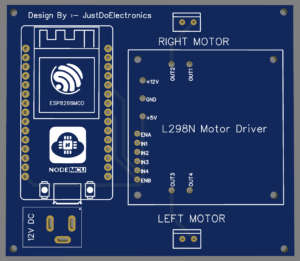
Ok, The L298N Motor Driver is Connected to the ESP8266 board. the 2 Bo motors are connected to the motor Driver Which is controlled via digital PWM Pins D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, And D5 of the ESP8266 Board.
PCB Design
We Will Design the PCB With the Help of EASYEDA Software
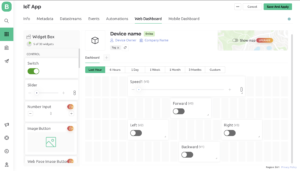
Blynk App
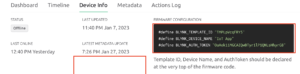
First, you have to set up a project in the Blynk app on your web dashboard and smartphone. after setting the app you receive an auth token which has to be provided in the code.
You can Download the Blynk app from the links below.
Open the Blynk App, register with an email ID, and then log in. After logging in, we will create a project. Enter all the details as shown Below
Mobile Application
Source Code / Program
The Source Code of the Grass cutting robot is Written in Arduino IDE software.
Before You Uploading The Code First Change a few Things.
- Auth
- Sid
- Pass
Next, connect this ESP8288 to the computer. Then create the program for this Project. First, download and install the libraries below.
- WIFI library
- Blynk library
|
1 2 3 |
char auth[] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"; char ssid[] = "Prateek"; char pass[] = "12345"; |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 |
#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> #include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h> //Motor PINs #define ENA D0 #define IN1 D1 #define IN2 D2 #define IN3 D3 #define IN4 D4 #define ENB D5 bool forward = 0; bool backward = 0; bool left = 0; bool right = 0; int Speed; char auth[] = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"; char ssid[] = "Prateek"; char pass[] = "12345"; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT); pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT); pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT); pinMode(IN3, OUTPUT); pinMode(IN4, OUTPUT); pinMode(ENB, OUTPUT); Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass, "blynk.cloud", 80); } BLYNK_WRITE(V0) { forward = param.asInt(); } BLYNK_WRITE(V1) { backward = param.asInt(); } BLYNK_WRITE(V2) { left = param.asInt(); } BLYNK_WRITE(V3) { right = param.asInt(); } BLYNK_WRITE(V5) { Speed = param.asInt(); } void smartcar() { if (forward == 1) { carforward(); Serial.println("carforward"); } else if (backward == 1) { carbackward(); Serial.println("carbackward"); } else if (left == 1) { carturnleft(); Serial.println("carfleft"); } else if (right == 1) { carturnright(); Serial.println("carright"); } else if (forward == 0 && backward == 0 && left == 0 && right == 0) { carStop(); Serial.println("carstop"); } } void loop() { Blynk.run(); smartcar(); } void carforward() { analogWrite(ENA, Speed); analogWrite(ENB, Speed); digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH); digitalWrite(IN3, HIGH); digitalWrite(IN4, LOW); } void carbackward() { analogWrite(ENA, Speed); analogWrite(ENB, Speed); digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); digitalWrite(IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(IN4, HIGH); } void carturnleft() { analogWrite(ENA, Speed); analogWrite(ENB, Speed); digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); digitalWrite(IN3, HIGH); digitalWrite(IN4, LOW); } void carturnright() { analogWrite(ENA, Speed); analogWrite(ENB, Speed); digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH); digitalWrite(IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(IN4, HIGH); } void carStop() { digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); digitalWrite(IN3, LOW); digitalWrite(IN4, LOW); } |
Project Demo
All images will show the proper working when we press the forward button this motor rotates in a clockwise direction if we press the backward button motor rotates in an anticlockwise direction.



Video Tutorial